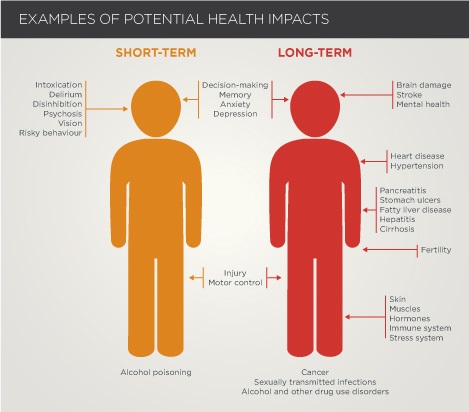
| | Conventional Medicine for Alcohol Addiction
Treatment methods for alcoholism can begin only when the alcoholic accepts that the problem exists and agrees to stop drinking. He or she must recognize that alcohol dependence is curable and must be driven to change. disease has 3 stages:
Detoxing (detox): This could be required right away after discontinuing alcohol use and can be a medical emergency, considering that detoxification can result in withdrawal seizures, hallucinations, delirium tremens (DT), and sometimes may lead to death.
Rehabilitation: This includes counseling and medications to supply the recovering alcoholic the skills needed for preserving sobriety. This phase in treatment can be conducted inpatient or outpatient. Both are equally successful.
Maintenance of sobriety: This phase's success mandates the alcohol ic to be self-motivated. The key to abstinence is moral support, which often includes routine Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) meetings and getting a sponsor.
Rehabilitation is often tough to maintain since detoxification does not alcohol ic.com/stop-drinking-alcohol/">quit the craving for alcohol . For an individual in an early stage of alcohol dependence, ceasing alcohol use may cause some withdrawal manifestations, including anxiety and poor sleep. Withdrawal from long-term dependence may induce uncontrollable trembling, convulsions, heightened anxiety, and the hallucinations of DTs. If not remedied professionally, individuals with DTs have a mortality rate of over 10 �so detoxing from late-stage alcohol addiction ought to be attempted under the care of an experienced physician and may necessitate a brief inpatient visit at a medical facility or treatment facility.
Treatment options might include one or additional medications. Benzodiazepines are anti-anxiety pharmaceuticals used to remedy withdrawal symptoms such as stress and anxiety and disrupted sleep and to defend against seizures and delirium. These are the most frequently used pharmaceuticals during the course of the detox cycle, at which time they are normally tapered and later discontinued. They should be used with care, since they might be addictive.
There are several medications used to assist individuals in rehabilitation from alcohol addiction sustain abstinence and sobriety. It conflicts with alcohol metabolism so that drinking even a little level will induce nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, confusion, and breathing troubles.
Another medicine, naltrexone, reduces the longing for alcohol. Naltrexone may be given even if the person is still drinking; nevertheless, just like all medicines used to treat alcoholism , it is suggested as part of an exhaustive program that teaches clients new coping skills. It is currently offered as a controlled release inoculation that can be given on a monthly basis.
Acamprosate is yet another medication that has been FDA-approved to lower alcohol craving.
Lastly, research indicates that the anti-seizure medicines topiramate and gabapentin may be useful in minimizing craving or anxiety during rehabilitation from alcohol consumption, although neither one of these pharmaceuticals is FDA-approved for the treatment of alcohol addiction.
medicationsAnti-anxietyor Anti-depressants drugs might be used to manage any underlying or resulting anxiety or melancholy, but since those syndromes might cease to exist with sobriety, the pharmaceuticals are usually not begun until after detoxification is finished and there has been some time of abstinence.
The objective of rehabilitation is total sobriety because an alcoholic remains vulnerable to relapse and possibly becoming dependent anew. Rehabilitation typically follows a Gestalt approach, which may consist of education and learning programs, group treatment, family members involvement, and involvement in support groups. Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is one of the most well known of the support groups, but other methods have also proved successful.

Diet and Nutrition for Alcoholism
Substandard health and nutrition goes along with alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence: Since an ounce of ethyl alcohol (the kind we drink) has additional than 200 calories but no nutritional benefit, consuming large quantities of alcohol tells the human body that it doesn't require additional nourishment. Problem drinkers are typically lacking in vitamins A, B complex, and C; folic acid; carnitine; selenium, zinc, and magnesium, along with important fatty acids and anti-oxidants. Strengthening such nutrients-- by offering thiamine (vitamin B-1) and a multivitamin-- can assist recovery and are a fundamental part of all detoxing regimens.
At-Home Treatments for Alcohol addiction
Sobriety is one of the most vital-- and probably the most hard-- steps to rehabilitation from alcoholism. To learn how to live without alcohol, you need to:
Avoid people and places that make consuming alcohol the norm, and discover new, non-drinking buddies.
Join a support group.
Get the help of family and friends.
Change your unfavorable reliance on alcohol with favorable dependences like a brand-new leisure activity or volunteer service with church or civic groups.
Start working out. Physical exercise releases substances in the brain that offer a "natural high." Even a walk following supper can be tranquilizing.
Treatment options for alcohol dependence can start only when the problem drinker acknowledges that the problem exists and agrees to stop drinking . For an individual in an early phase of alcoholism, ceasing alcohol use might result in some withdrawal manifestations, consisting of anxiety and disturbed sleep. If not treated professionally, individuals with DTs have a mortality rate of more than 10 �so detoxification from late-stage alcohol addiction should be attempted under the care of a skillful physician and might necessitate a short inpatient stay at a hospital or treatment center.
There are numerous medications used to assist individuals in recovery from alcoholism sustain abstinence and sobriety. Poor health and nutrition goes with heavy alcohol consumption and alcoholism : Because an ounce of alcohol has more than 200 calories but no nutritional value, ingesting serious levels of alcohol tells the body that it doesn't need more nourishment.
| | | |
|